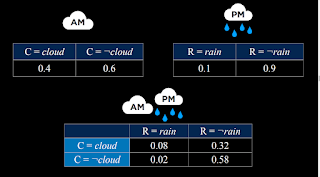
Baysian analysis allows for joint probability, below:
If I add the two columns, I get back to the 'rain in the afternoon' set of probabiities.
If I add across rows, I return to the 'clouds in the morning' numbers. So what is likely to
happen on any given day: no cloud and no rain; cloud and no rain; cloud and rain;
no cloud and rain. In that order...
* * *
I can also ask a 'time-inverted' question. What is the probability of having experienced
cloud in the morning , given it is raining in the afternoon.
Alpha, here, is used to produce a standard probability distribution that adds to 1!
* * *
Just nstalled pomegranate, a probabilistic programming library for python.
Tomorrow...


No comments:
Post a Comment